|
Introduction In the last fifteen years, the fast increase of the processing power of low-cost computers and the rapid development of high-speed networking technologies have boosted the diffusion of distributed computing environments for solving complex problems. The expression grid computing has become popular to denote the set of distributed computing techniques that works over a great loosely-coupled virtual supercomputer, formed by putting together many heterogeneous components of different characteristics and computing power. This infrastructure has made it feasible to provide more pervasive and cost-effective access to a collection of distributed computer resources for solving large problems [Foster and Kesselman, 1998]. A key problem when using a distributed computing environment consists in finding a planning strategy or scheduling of a set of tasks to be executed, in order to assign the computational resources in a smart way, by satisfying some efficiency criteria. This website describes the Heterogeneous Computing Scheduling Problem (HCSP), its mathematical formulation, and concepts the problem instances already used in the related literature as well as new problem instances specifically created in our workgroup. |
|
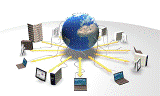
Heterogeneous Computing Environments A heterogeneous computing (HC) system is a well-orchestrated and coordinated set of processing elements (often called resources, processors or simply machines), interconnected by a network. The heterogeneous quality of the computing environment refers to the variable computational capabilities of both the machine pool and the interconnection technology (e.g., CPUs processing power, data transfer speed of the network, etc.). Usually, a HC system comprise a parallel and/or distributed suite of high-performance machines, working together in order to provide support for cooperatively solving computationally-intensive applications with diverse computing requirements. Since the massive popularization of parallel and distributed computing in the decade of 1990, HC have emerged as a major paradigm for scientific and high performance applications. HC systems have been employed to solve key problems with high computational requirements in many application areas [Khokhar et al., 1993; Freund et al., 1994; Eshaghian, 1996; Braun et al., 2000]. A crucial problem for HC systems consists in finding a suitable assignation of tasks to machines in order to satisfy some objectives related with efficiency, resource usage, economic profit, and many others criteria. This problem, called task assignment, task planning or scheduling, has been an important focus in this line of research in the last two decades. |
|
HCSP |
|
Heterogeneous Computing Scheduling Problem |
|
Main page |